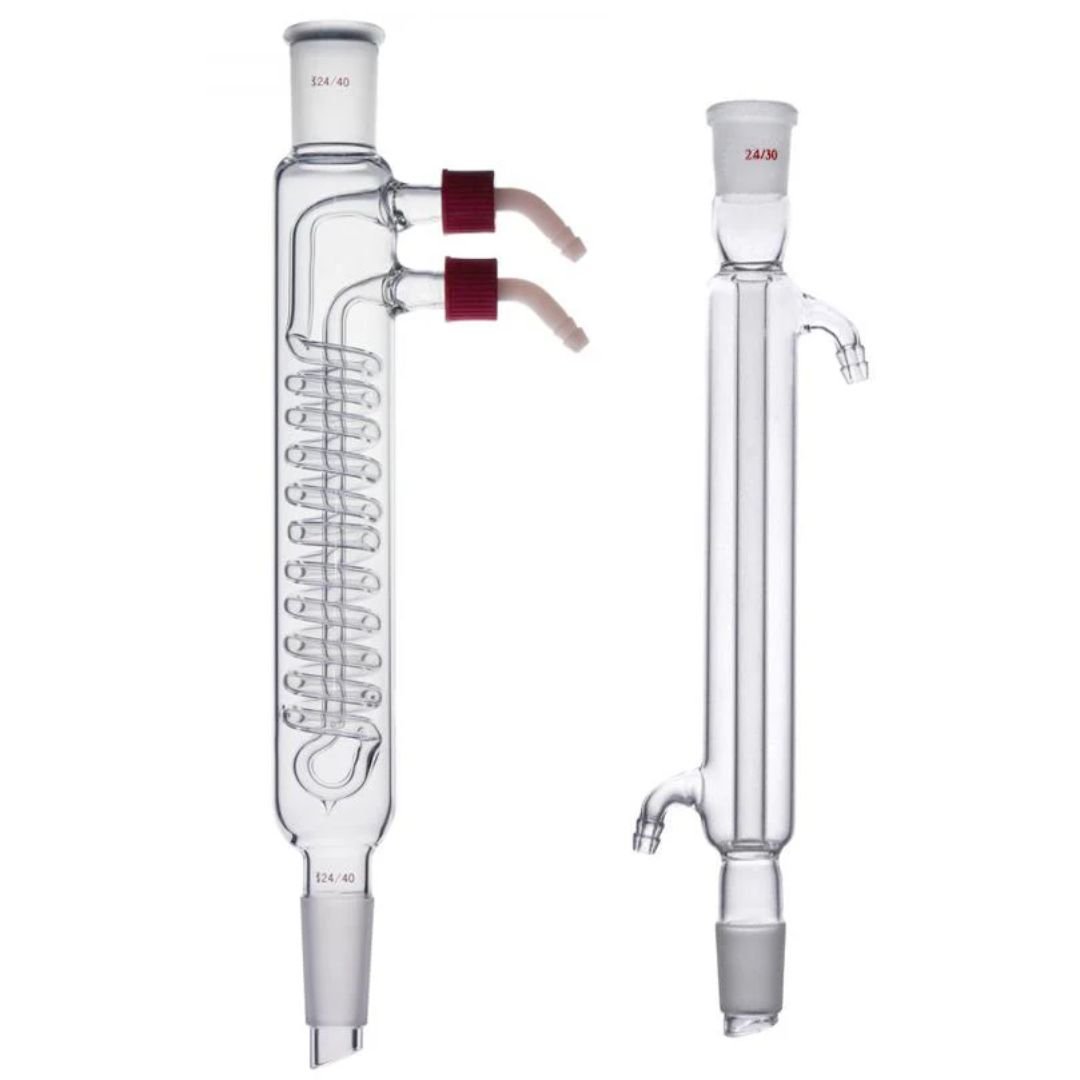
A condenser is a critical piece of laboratory glassware used in distillation processes to cool and condense vapors back into liquid form. Commonly made from borosilicate glass for its thermal and chemical resistance, condensers are typically used in organic chemistry and industrial applications where the separation and purification of liquids are required.
The condenser features a long, cylindrical body with an inner tube where vapor travels and an outer jacket where coolant, usually water, circulates. The coolant absorbs the heat from the vapor, causing it to condense into a liquid that can be collected. There are various types of condensers, including Liebig, Allihn (bulb), and Graham (coil), each designed for specific cooling efficiency and application needs.
Condensers are essential in procedures such as reflux, fractional distillation, and rotary evaporation, where precise temperature control and efficient heat exchange are vital. Their robust construction and efficient design make them indispensable in both academic and industrial laboratories.










Reviews
There are no reviews yet.